Background of Company:
UGO taxi & Mini Bus Company is better known, as UGO taxis are hire agents in Bristol. This company also hire for tour, Minibus, wedding limousine car. For historic tours and highland bus hire as well as coach hire come to Coach Company and Bus Company that knows the area. This company offers interesting sightseeing tours, either shared or personal, to make the most of your stay in beautiful Bristol city. This company also takes great pride in offering a personal service to all customers.
The company has plans to expand into other areas in UK by acquisition of small exciting taxi or Minibus hire companies, increasing business performance by improving servicing processes are a rapidly growing area of interest and one which typically generates very substantial business benefits. The company has simple booking system and it senior management realised to improve the business activities. The company’s operation manager wants to new IT system to introduce best practices into the organisation. UGO taxi for which I have created the IDEF model is a medium sized taxi and bus company. It involved in a business that provides quality transport service for pre booked journey for individuals and groups. The company business is growing that made company to face difficulty to maximise the efficiency and quality of service, the company while maintaining and the flexibility and responsiveness to the demand generator.
*Low resource utilisation which means the vehicle is idle and capital is tied up needlessly.
*High unplanned overtime levels which are forced by the need to get late running orders delivered.
*Too much stock which leads to excess capital tied up, too many vehicles are in hand but not being used effectively.
*A high level of late service deliveries which gives many problems, including inability to retain customers and more expensive service costs.
*Inability to identify which impact of changes to the service plan such as additional, high priority orders and mechanical failure.
*High cost of labour with many periods when labour is idle.
Forecasting model of UGO:
Forecasting is the predication, projection or estimation of uncertain future events or levels of activities. It is basic to planning that represents the preparation of budget and is concerned with probable events. The future is uncertain and numerous techniques, numerical or statically formula and assumption have to try and limit the amount of uncertainty. Probability theory is the one statically method that is used very widely in many business organisation. Forecast enables to develop a clear plan and the right objectives to select.
Forecast can make UGO management think ahead and give a singleness of purpose to planning by concentrating attention on the future. It is also the foundation of company’s entire logistics process. It can be affected by many factors which include trends relating to the general economy, political, international, the strength of competitors and servicing cost trend. The items which can affect forecasting in UGO are:
#Political stability;
#Population trends;
#Price levels;
#Government controls and fiscal policy;
#Employment, service and company income;
#Technical environment- i.e. computers, IT and the impact of speed of developments.
In the process of forecasting in UGO, it is important to stress the need to examine the economic environment and possible fluctuations in the company profits and relationships to possible cycles to business activity.
UGO is going to plan for longer periods (i.e. 10 years) because it is going to implement computer and IT, a forecast of technological changes is vital for it. The revision is continually made of the basic assumptions on which the plans were based, as circumstances change and thus new plans would be developed. It is important to be familiar with the five major characteristics of demand forecasting which are:
*Average: Demand trends to cluster around a specific level.
*Trend: demand consistently increases or decreases over time.
*Seasonality: demand shows peaks and valley at consistent intervals. These intervals can be hours, days, week, months, years or seasons.
*Cyclical: Demand gradually increases and decreases over an extended period of time, such as years. Business cycles (recession and expansion) and service life cycles influence this component of demand.
*Random error: Variations that cannot be explained or predicated.
The magnitude of the error, referred to as forecast accuracy, is what determines whether the forecasts are good or bad. Careful selection of appropriate forecasting techniques and the best practices will help business improve forecast accuracy.
There are number of approaches available in the forecasting methods. These range from extrapolation of trends of technology to more advanced methods such as
Subjective or judgement method: This method utilise opinions to develop forecasts and generally used when historic data is not available. The basic for judgement methods is that the decision maker possesses sufficient experience to establish forecasts. In general, they are low cost and have rapid development time. However, they are not consistently accurate and subject to bias by group creating the forecast.
#Delphi technique which is a procedure for arriving at a consensus of opinion among a group of experts, who are given a detailed questionnaire about a problem. They give written opinions that are everyone reads the opinions of others and can revise their own ideas. Direct contact and debate is avoided purposively as this may produce hasty attachment to some ideas.
#Brainstorming usually involves conducting a group meeting on a problem and any idea is welcomed, however strange. The hope is that many ideas may be generated as there is freedom to let idea flow, and from these, positive solutions may emerge.
#Scenario construction is a method used to make long-range forecasts. It is a logical description of events. The committee or ‘think-tank’ examines details of alternative events. A well-constructed scenario exploring each adjustment or re-adjustment may produce a reasonably accurate forecast.
#Sales force estimation which is closest to the customer and immersed in the marketplace, creates estimates of customer demand. Because of their proximity to the customers, information from the sales force can be very reliable. However, individual biases and can decrease the effectiveness of this technique.
#Executive opinion that usually have a good understanding of the broad-based factors that influence demand, create estimates of customer demand. This can be good method to use when creating forecasts for new or very strategic product or service. However, it consumes valuable executive time and requires consensus between executives.
Causal (Econometric) is a newer development in forecasting. This is done through the construction of mathematical models in which various factors of the economy are given mathematical values and their effect upon each other ascertained through the solution of equations. The level of country’s economy is of course a vital factor upon which a company’s sales and revenue plans are based.
In other word, Causal methods create forecasts by determining a cause-effect relationship between independent variables and the demand for the service. Two examples where casual methods could be used to create forecasts will help to illustrate this:
#Forecasting MIS: Long-range forecasts for UGO Taxi Company can be used to forecast IT used or accessed IS by customers.
#Promotion planning: if the customer price of product is reduced by 1.50 per unit, how will it affect demand?
One of the benefits is that causal methods provide good long term forecast accuracy. However, the forecasts are only as good as the independent variables identified and the model created. They require careful thought and insight into the variables that effect demand.
#Linear Regression (Simple and Multiple):
Simple liner regression generates a forecast by linking one independent variable to the demand for the product or service. For example, demand or order of taxi may be dependent on the fare that is charged for the service. A model would be developed which described this relationship. Given a specific demand or order, a demand forecast for UGO taxi will be generated.
Multiple linear regressions generate a forecast by linking two or more independent variables to the demand for the service. For example, Order of taxi is may be dependent on the fare that is charged for the service, the quality of service and customer pick-up time. A model would be developed which described this relationship. Given a specific order or demand, fare, quality of service and pick-up time for UGO taxi will be generated.
Time Series analysis is a procedure which identifies information which forms patterns over a period of time. A projection is made by extrapolation from past experience. Trends for the past years are noted and projected into the future. In the short term, it performs very well; in long term, it generally performs poorly. These techniques are best used for (a) mature products, (b) products with a large amount of historical data, or (c) products with smooth, random demand variations.
Demand forecasting software easily systematises these forecasting methods. Because of this, forecasting large number of items by these methods is easily performed with software.
#Naïve is a simple forecasting technique for the next period is equal to the demand for the current period. This is a simple, low-cost method that only takes trend into account. However, if demand is variable, this is a poor method to use.
#Moving average (simple and weighted): A simple moving average method is used to determine the average amount of demand over a given period. The weighted moving average technique allows each period in the calculation to carry its own weight. UGO can specify that recent demand will be weighted more heavily in the calculation than older data.
Moving average techniques are most appropriate for stable demand patterns, when demand does exhibits trend or seasonality components. Unfortunately, if trend or seasonality exists in the demand, the forecasts will lag in their ability to predict future demand.
#Exponential Smoothing (Single, double, triple): Exponential smoothing methods require user-specified factors to calculate the forecast:
*Smoothing (averaging): reactivity of forecast to current demand period.
*Trend: dampen or accelerate trend in the forecast.
*Seasonality: dampen or enhance the effect of seasonality on the forecast.
Single exponential smoothing uses the smooth factor only in the forecast calculation. Double exponential smoothing uses the smoothing and trend factors in the forecast calculation. Triple exponential smoothing uses the smoothing, trend and seasonality factors in the forecast calculation. These techniques are popular and easily calculated with demand planning software. These performs well in short term forecasts, it does not perform as well on products with low demand.
The graphs and data plotted from the forecasting table shows the class of domain as below. Since the company which was operation on existing data and of which it was realised need of IT based system should introduce to import efficiency of company. After critical analysis on the outmoded operational sequence, it was identified that the drop of demand was very low at a particular period on the previous operation.
Furthermore to improve the existing system, demand pattern, EWMA, EWMA ABC, Period, Seasonal forecast, trend forecast, trend and seasonality enhanced forecast (TSEF), were calculated to show a solid improvement in the new demand. The new demand plotted clearly shows how the performances will determine the actual demand of the period. This actually synchronise with IDEF model to produce the fitted ERP system. The forecasting table shows that the demand of the ready existing data is lower than the new demand.
IDEF model of UGO taxi:
IDEF0 is used to produce a “function model” which is a structured representation of the activities or processes within the environment or system. In every manufacturing or service organisation there is a variety of reason to improve the system but in this context of UGO taxi, we can define as (1) competition within the market is demanding more competitive systems which can operate upper limits of productivity. (2) Customers are become more demanding so that requiring new service systems to become more flexible and have shorter lead-time. (David Osullivan 25 March 1991).
IDEF is a structured technique that has become synonymous with the design of manufacturing systems is the Icam (Integrated computer Aided Manufacturing) programme. IDEF0 is that complex systems can be described in terms of the activities performed in the system and in such a way as to expose detail progressively through a hierarchical decomposition. IDEF0 in fact closely reflect the activity modelling part of the SADT methodology. (David Osullivan).
A model of UGO IDEF0 is a representation of a set of components of a system area. This model is developed for understanding, analysis, improvement or replacement of the system. Systems are composed of interfacing or interdependent parts that work together to perform a useful function. System parts which can be any combination of things, including people, information, software, processes, equipment, products, or raw materials. The model describes what a system does, what controls it, what things it works on, what means it uses to perform its functions, and what it produces.
IDEF0 is a modelling technique based on combined graphics and text that are presented in an organized and systematic way to gain understanding, support analysis, provide logic for potential changes, specify requirements, or support systems level design and integration activities in UGO. An IDEF0 model is composed of a hierarchical series of diagrams that gradually display increasing levels of detail describing functions and their interfaces within the context of a system.
IDEF0 is an engineering technique for performing and managing needs analysis, benefits analysis, requirements definition, functional analysis, systems design, maintenance, and baselines for continuous improvement. IDEF0 models provide a "blueprint" of functions and their interfaces that must be captured and understood in order to make systems engineering decisions that are logical, affordable, Integra table and achievable. The IDEF0 model of UGO taxi reflects how system functions interrelate and operate just as the blueprint of a product reflects how the different pieces of a product fit together. The goal is improve the management of tangible and intangible assets according to UGO’s a along range plan development of new system comprising and this IDEF diagram of UGO’s taxi has presented to illustrate how the IDEF0 and IDEF1 structure can be applied in Service Company like UGO Taxi CompanyBackground of Company:
UGO taxi & Mini Bus Company is better known, as UGO taxis are hire agents in Bristol. This company also hire for tour, Minibus, wedding limousine car. For historic tours and highland bus hire as well as coach hire come to Coach Company and Bus Company that knows the area. This company offers interesting sightseeing tours, either shared or personal, to make the most of your stay in beautiful Bristol city. This company also takes great pride in offering a personal service to all customers.
The company has plans to expand into other areas in UK by acquisition of small exciting taxi or Minibus hire companies, increasing business performance by improving servicing processes are a rapidly growing area of interest and one which typically generates very substantial business benefits. The company has simple booking system and it senior management realised to improve the business activities. The company’s operation manager wants to new IT system to introduce best practices into the organisation. UGO taxi for which I have created the IDEF model is a medium sized taxi and bus company. It involved in a business that provides quality transport service for pre booked journey for individuals and groups. The company business is growing that made company to face difficulty to maximise the efficiency and quality of service, the company while maintaining and the flexibility and responsiveness to the demand generator.
Low resource utilisation which means the vehicle is idle and capital is tied up needlessly.
High unplanned overtime levels which are forced by the need to get late running orders delivered.
Too much stock which leads to excess capital tied up, too many vehicles are in hand but not being used effectively.
A high level of late service deliveries which gives many problems, including inability to retain customers and more expensive service costs.
Inability to identify which impact of changes to the service plan such as additional, high priority orders and mechanical failure.
High cost of labour with many periods when labour is idle.
Description of model:
At the centre of the business is the newly designed computer based ERP system which is an integrated system. IDEF model is the approach towards the implementation to restructure the company to produce and efficient and effective operation cycle- input, control, resource and output carries the real function which will determine the validity of the transformation in the company. It collects data from different functional areas of company such as: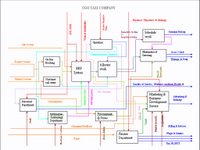

 The inputs data are:
The inputs data are:
Regular customers, Ordinary customers
Sales revenue,
Market & service feedback,
Fare,
Fuel, Spare parts etc.
The Control Inputs are:
Vehicle availability,
Service response time,
Business objective & strategy,
ISO 9000
The Resource inputs are:
Computer hardware & software,
Sub company acquisition,
Market research,
New vehicles,
Consumable goods and parts,
Staff & drivers,
Information technology & wireless.
The outputs are:
GPS, www, wireless, free phone,
Customers pick up service,
Publicity and advertising,
Quality service, health & Safety,
Billing and Invoices,
Wastage and scrape,
Wages, salaries & other expanses,
Job creation,
Tax, NI, Vehicle Insurance, MOT,
Service Vehicle.
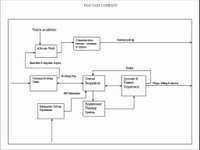
The raw data of inputs, control inputs and resource inputs to the business that produce output which has shown in IDEF0 model. The company is driven by demand, which may include customers order or sales order forecast. The overall situation can be shown in the attached IDEF model diagram. UGO taxi’s daily basis operation process, the company has launched its new IT based server to make work more effective and reliable.
Business objective and strategy: The ideal is for UGO Company to formulate specific objectives and develop policies, within the frame of general objectives, which together result in co-ordinated and controlled, decision making. To be able to survive, UGO must earn sufficient profits to sell services, of certain quality, at competitive price. A newer approach to consideration of objectives is the ‘stakeholder’ theory which suggests that UGO has responsibility to maintain an equitable and working balance among the claims of the interested groups, i.e. stockholders, employees, customers, suppliers, vendors and the public.
Booking system: UGO has provided various communication services to the customer for booking services. Customer can book their taxi, minibus, wedding limousine car tour and so on through the internet, direct communication with driver, free phone and so on. Customer can access internet and get more and more information which can help them to get information about the company policy and services. They can book through internet which would be cheaper and efficient for customer and the company. It can help the company to maintained the data about the customer i.e. customer status (medium class or rich class, quality oriented or general customer, area and location etc) that can help to company to make future planning and strategy.
Feedback: Feedback involves passing information from one point in a system back to an earlier point with a view to modifying behaviour. Feedback is connected with planning, with its determination of instructions to be used as directives for activities, and the standards for comparison. Control comes from comparison with standards showing the need for corrective action, and analysis of deviation so future plan can be readjusted. The UGO can collect the customer feedback through different source i.e. internet user customer, regular customer, drivers and market survey which will help it for future business planning and service.
Fare: Fare is the main resource for UGO business success. It would depend on the company policy that which type of customer that company has targeted in the market. There would be variety of customer and each customer has different sort of demand, in this case fare would play very vital role. Customer can get information about the fare while they are booking the taxi or minibus through call centre, company’s web site. That will help them to fast and quick information to decide their needs.
Fuels and spares parts: The taxi company always need fuel and the spare parts for driving, maintenance and vehicle servicing. Company can keep data and save millions of pound through this department by keeping the data about the Fuels consumed, Spare parts and the vehicle servicing.
Control and call centre: Control is the back bone of this company in which most of the process is done in this department. Most of the information would be held in this department to give the quality and reliable service to the customer. This department will deal with customer, drivers as well as company’s other department to make the service reliable and convey correct data at correct time by using different IT system e.g. GPS which will help to give the data about the driver’s current position and mileage they travelled, company’s website will help to take customer’s order and feedback which will very important to marketing department. The controller mobilise the driver and try to give good service as customer required.
Allocate work: It deals with the long term request as well as immediate booking. The control IT department can relay that information within a twinkle of an eye by sophisticated computerised system and provide service in the right time with quality service. The company’s IT department can allocate the job to driver by using the software which can help to allocate fast and correct at the right time.
Schedule work:In this process, the company use to allocate the duty and the rota for the driver to give the service. It is basically deal with fleets, company fleet schedule for servicing or repairs more especially due date or period. It handles long term customer request. The company can keep all the data in computer that could help in the future purpose.
Finance department: Finance department generally involve in different operation process i.e. tariff (Fares), buy fuel & spare parts, prepare budget for the taxi company and so on. This department can keep all this information and provide the different information with database to all interested parties. The company’s financial department will keep the employees database and their salaries, vehicle’s database and its associated things which will help to give information to other department in the right time with correct information.
Marketing department: The marketing department generally involved in promotion and advertising. The different associated data and information from different will help the marketing department to do promotion and advertising. Company can target different customer by promoting company’s policy and service. The marketing department associated with job advertising which will help the current market’s for job. The current IT service will help to create job and it will make interested and make the goodwill of company.
ISO 9000: The Company has decided to implement ISO 9000 which will help all the department, staffs and customer to provide correct information and the work in balance and filed. The company will take health, safety and the environment (HSE) issues extremely seriously at the highest level. Safety is always the first item on any work. The company has also going to implement policy which is based on following principle:
*Risk reduction is everyone’s responsible,
*Awareness, involvement and support of all staffs, drivers and customers is essential when identifying hazards and assessing and controlling risks,
*Continuous improvement must be the way of life, with business setting goals and measurements to drive progress.
*To reduce risk and road accident, company will issue driver’s hours and techno graphs.
The business process of UGO can be affected by different factors which have mentioned earlier as well. The business problems listed earlier obviously have successful scheduling system which is essential to develop a detailed, agreed definition of the business problem and enhance of the business process and its associated issues. In addition to consider the physical operations of scheduling within the company and the various business issues included information system. There are two types of information required which may be supplied by other systems, or in some case directly entered into the scheduling system itself. The two types of scheduling system are:
Static data
Number of vehicles,
Number of drivers,
Routes.
Dynamic data
Traffic congestions,
Available vehicles,
Available drivers.
Benefits:
The typical benefits of IDEF model based on demand forecasting of UGO taxi are list below:
Fuel efficiency,
Reduced idle time,
On time pick up and drop,
Efficient allocation of job,
Job creation in the market (Professional)
There are also large numbers of less quantifiable benefits, such as;
Increased quality of service
Reduce response time to customer
Ability to promise pick up
Capacity analysis, e.g. Ability to identify bottlenecks in the systems expansion,
Reaction to problems, e.g. identification of impact of breakdown of vehicles,
Prediction of problems, e.g. where on line booking is linked to a booking control system and can continually re schedule to identify predicted changes in service response as conditions on the any mishap.
The need for IT systems:
The need to improve competitive position is driven by various factors. Some of the most prominent of these are:
National competition: Many taxi companies are finding that they must improve efficiency and service considerably in order to compete with emerging service providers in their marketplace.
Ready to use vehicle: Timeless availably of well maintained and serviced vehicles to provide service is now insisted upon far more than new in many modern companies where quality of service has become the norm.
Increasing service range: market forces are leading to rapid increase in the number of new services which a business must provide.
Based on the keys factors of demand forecasting and IDEF model, we can develop the important technical features and properties from which we can realise the full potential and value of demand.
Conclusion:
The computer based scheduling and demand forecasting system has come of age for almost survive providing sector. Those companies which adopt it can improve their business performance in many areas. Together, these usually provide substantial commercial company is using an on line booking system as well as customer call centre. All the booking information goes into the booking system and then into the central database from where all the data is used by different functional areas. Scheduling system is a system that receives booking information and then plans the work accordingly and gives on-screen schedules to the operations people, so that they can allocate work to the drivers. All the details pertaining to the best shortest routines to the destinations, traffic congestions, mileage, number of vehicles available, number of drivers available, status of vehicles in the maintenance department for serving all that information is available to them by scheduling system.
Conversely, any company which does not optimise its decision support in this area is at immediate disadvantage. The gap between users and non users can only increase as service demands increase, leading to poorer performance and eventually collapse.
Refrences:
Appleby, Robert C, 1991, Modern Business Administration, Pitman Publishing, London WC2E 9AN
International Journal of Project management Vol.20, No.3 April 2002, page 194
International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Vol. 7, No.2, March-April, 1994, page 101
International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Vol.14, No.5, sept-Oct 2000, page 473
International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, vol. 11, no.5, sept-oct 1998 page.416
International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, vol.6 no.4 july-Augt. 1993, page 252
http://www.boc.com/
http://www.gistworld.com/
UGO taxi & Mini Bus Company is better known, as UGO taxis are hire agents in Bristol. This company also hire for tour, Minibus, wedding limousine car. For historic tours and highland bus hire as well as coach hire come to Coach Company and Bus Company that knows the area. This company offers interesting sightseeing tours, either shared or personal, to make the most of your stay in beautiful Bristol city. This company also takes great pride in offering a personal service to all customers.
The company has plans to expand into other areas in UK by acquisition of small exciting taxi or Minibus hire companies, increasing business performance by improving servicing processes are a rapidly growing area of interest and one which typically generates very substantial business benefits. The company has simple booking system and it senior management realised to improve the business activities. The company’s operation manager wants to new IT system to introduce best practices into the organisation. UGO taxi for which I have created the IDEF model is a medium sized taxi and bus company. It involved in a business that provides quality transport service for pre booked journey for individuals and groups. The company business is growing that made company to face difficulty to maximise the efficiency and quality of service, the company while maintaining and the flexibility and responsiveness to the demand generator.
*Low resource utilisation which means the vehicle is idle and capital is tied up needlessly.
*High unplanned overtime levels which are forced by the need to get late running orders delivered.
*Too much stock which leads to excess capital tied up, too many vehicles are in hand but not being used effectively.
*A high level of late service deliveries which gives many problems, including inability to retain customers and more expensive service costs.
*Inability to identify which impact of changes to the service plan such as additional, high priority orders and mechanical failure.
*High cost of labour with many periods when labour is idle.
Forecasting model of UGO:
Forecasting is the predication, projection or estimation of uncertain future events or levels of activities. It is basic to planning that represents the preparation of budget and is concerned with probable events. The future is uncertain and numerous techniques, numerical or statically formula and assumption have to try and limit the amount of uncertainty. Probability theory is the one statically method that is used very widely in many business organisation. Forecast enables to develop a clear plan and the right objectives to select.
Forecast can make UGO management think ahead and give a singleness of purpose to planning by concentrating attention on the future. It is also the foundation of company’s entire logistics process. It can be affected by many factors which include trends relating to the general economy, political, international, the strength of competitors and servicing cost trend. The items which can affect forecasting in UGO are:
#Political stability;
#Population trends;
#Price levels;
#Government controls and fiscal policy;
#Employment, service and company income;
#Technical environment- i.e. computers, IT and the impact of speed of developments.
In the process of forecasting in UGO, it is important to stress the need to examine the economic environment and possible fluctuations in the company profits and relationships to possible cycles to business activity.
UGO is going to plan for longer periods (i.e. 10 years) because it is going to implement computer and IT, a forecast of technological changes is vital for it. The revision is continually made of the basic assumptions on which the plans were based, as circumstances change and thus new plans would be developed. It is important to be familiar with the five major characteristics of demand forecasting which are:
*Average: Demand trends to cluster around a specific level.
*Trend: demand consistently increases or decreases over time.
*Seasonality: demand shows peaks and valley at consistent intervals. These intervals can be hours, days, week, months, years or seasons.
*Cyclical: Demand gradually increases and decreases over an extended period of time, such as years. Business cycles (recession and expansion) and service life cycles influence this component of demand.
*Random error: Variations that cannot be explained or predicated.
The magnitude of the error, referred to as forecast accuracy, is what determines whether the forecasts are good or bad. Careful selection of appropriate forecasting techniques and the best practices will help business improve forecast accuracy.
There are number of approaches available in the forecasting methods. These range from extrapolation of trends of technology to more advanced methods such as
Subjective or judgement method: This method utilise opinions to develop forecasts and generally used when historic data is not available. The basic for judgement methods is that the decision maker possesses sufficient experience to establish forecasts. In general, they are low cost and have rapid development time. However, they are not consistently accurate and subject to bias by group creating the forecast.
#Delphi technique which is a procedure for arriving at a consensus of opinion among a group of experts, who are given a detailed questionnaire about a problem. They give written opinions that are everyone reads the opinions of others and can revise their own ideas. Direct contact and debate is avoided purposively as this may produce hasty attachment to some ideas.
#Brainstorming usually involves conducting a group meeting on a problem and any idea is welcomed, however strange. The hope is that many ideas may be generated as there is freedom to let idea flow, and from these, positive solutions may emerge.
#Scenario construction is a method used to make long-range forecasts. It is a logical description of events. The committee or ‘think-tank’ examines details of alternative events. A well-constructed scenario exploring each adjustment or re-adjustment may produce a reasonably accurate forecast.
#Sales force estimation which is closest to the customer and immersed in the marketplace, creates estimates of customer demand. Because of their proximity to the customers, information from the sales force can be very reliable. However, individual biases and can decrease the effectiveness of this technique.
#Executive opinion that usually have a good understanding of the broad-based factors that influence demand, create estimates of customer demand. This can be good method to use when creating forecasts for new or very strategic product or service. However, it consumes valuable executive time and requires consensus between executives.
Causal (Econometric) is a newer development in forecasting. This is done through the construction of mathematical models in which various factors of the economy are given mathematical values and their effect upon each other ascertained through the solution of equations. The level of country’s economy is of course a vital factor upon which a company’s sales and revenue plans are based.
In other word, Causal methods create forecasts by determining a cause-effect relationship between independent variables and the demand for the service. Two examples where casual methods could be used to create forecasts will help to illustrate this:
#Forecasting MIS: Long-range forecasts for UGO Taxi Company can be used to forecast IT used or accessed IS by customers.
#Promotion planning: if the customer price of product is reduced by 1.50 per unit, how will it affect demand?
One of the benefits is that causal methods provide good long term forecast accuracy. However, the forecasts are only as good as the independent variables identified and the model created. They require careful thought and insight into the variables that effect demand.
#Linear Regression (Simple and Multiple):
Simple liner regression generates a forecast by linking one independent variable to the demand for the product or service. For example, demand or order of taxi may be dependent on the fare that is charged for the service. A model would be developed which described this relationship. Given a specific demand or order, a demand forecast for UGO taxi will be generated.
Multiple linear regressions generate a forecast by linking two or more independent variables to the demand for the service. For example, Order of taxi is may be dependent on the fare that is charged for the service, the quality of service and customer pick-up time. A model would be developed which described this relationship. Given a specific order or demand, fare, quality of service and pick-up time for UGO taxi will be generated.
Time Series analysis is a procedure which identifies information which forms patterns over a period of time. A projection is made by extrapolation from past experience. Trends for the past years are noted and projected into the future. In the short term, it performs very well; in long term, it generally performs poorly. These techniques are best used for (a) mature products, (b) products with a large amount of historical data, or (c) products with smooth, random demand variations.
Demand forecasting software easily systematises these forecasting methods. Because of this, forecasting large number of items by these methods is easily performed with software.
#Naïve is a simple forecasting technique for the next period is equal to the demand for the current period. This is a simple, low-cost method that only takes trend into account. However, if demand is variable, this is a poor method to use.
#Moving average (simple and weighted): A simple moving average method is used to determine the average amount of demand over a given period. The weighted moving average technique allows each period in the calculation to carry its own weight. UGO can specify that recent demand will be weighted more heavily in the calculation than older data.
Moving average techniques are most appropriate for stable demand patterns, when demand does exhibits trend or seasonality components. Unfortunately, if trend or seasonality exists in the demand, the forecasts will lag in their ability to predict future demand.
#Exponential Smoothing (Single, double, triple): Exponential smoothing methods require user-specified factors to calculate the forecast:
*Smoothing (averaging): reactivity of forecast to current demand period.
*Trend: dampen or accelerate trend in the forecast.
*Seasonality: dampen or enhance the effect of seasonality on the forecast.
Single exponential smoothing uses the smooth factor only in the forecast calculation. Double exponential smoothing uses the smoothing and trend factors in the forecast calculation. Triple exponential smoothing uses the smoothing, trend and seasonality factors in the forecast calculation. These techniques are popular and easily calculated with demand planning software. These performs well in short term forecasts, it does not perform as well on products with low demand.
The graphs and data plotted from the forecasting table shows the class of domain as below. Since the company which was operation on existing data and of which it was realised need of IT based system should introduce to import efficiency of company. After critical analysis on the outmoded operational sequence, it was identified that the drop of demand was very low at a particular period on the previous operation.
Furthermore to improve the existing system, demand pattern, EWMA, EWMA ABC, Period, Seasonal forecast, trend forecast, trend and seasonality enhanced forecast (TSEF), were calculated to show a solid improvement in the new demand. The new demand plotted clearly shows how the performances will determine the actual demand of the period. This actually synchronise with IDEF model to produce the fitted ERP system. The forecasting table shows that the demand of the ready existing data is lower than the new demand.
IDEF model of UGO taxi:
IDEF0 is used to produce a “function model” which is a structured representation of the activities or processes within the environment or system. In every manufacturing or service organisation there is a variety of reason to improve the system but in this context of UGO taxi, we can define as (1) competition within the market is demanding more competitive systems which can operate upper limits of productivity. (2) Customers are become more demanding so that requiring new service systems to become more flexible and have shorter lead-time. (David Osullivan 25 March 1991).
IDEF is a structured technique that has become synonymous with the design of manufacturing systems is the Icam (Integrated computer Aided Manufacturing) programme. IDEF0 is that complex systems can be described in terms of the activities performed in the system and in such a way as to expose detail progressively through a hierarchical decomposition. IDEF0 in fact closely reflect the activity modelling part of the SADT methodology. (David Osullivan).
A model of UGO IDEF0 is a representation of a set of components of a system area. This model is developed for understanding, analysis, improvement or replacement of the system. Systems are composed of interfacing or interdependent parts that work together to perform a useful function. System parts which can be any combination of things, including people, information, software, processes, equipment, products, or raw materials. The model describes what a system does, what controls it, what things it works on, what means it uses to perform its functions, and what it produces.
IDEF0 is a modelling technique based on combined graphics and text that are presented in an organized and systematic way to gain understanding, support analysis, provide logic for potential changes, specify requirements, or support systems level design and integration activities in UGO. An IDEF0 model is composed of a hierarchical series of diagrams that gradually display increasing levels of detail describing functions and their interfaces within the context of a system.
IDEF0 is an engineering technique for performing and managing needs analysis, benefits analysis, requirements definition, functional analysis, systems design, maintenance, and baselines for continuous improvement. IDEF0 models provide a "blueprint" of functions and their interfaces that must be captured and understood in order to make systems engineering decisions that are logical, affordable, Integra table and achievable. The IDEF0 model of UGO taxi reflects how system functions interrelate and operate just as the blueprint of a product reflects how the different pieces of a product fit together. The goal is improve the management of tangible and intangible assets according to UGO’s a along range plan development of new system comprising and this IDEF diagram of UGO’s taxi has presented to illustrate how the IDEF0 and IDEF1 structure can be applied in Service Company like UGO Taxi CompanyBackground of Company:
UGO taxi & Mini Bus Company is better known, as UGO taxis are hire agents in Bristol. This company also hire for tour, Minibus, wedding limousine car. For historic tours and highland bus hire as well as coach hire come to Coach Company and Bus Company that knows the area. This company offers interesting sightseeing tours, either shared or personal, to make the most of your stay in beautiful Bristol city. This company also takes great pride in offering a personal service to all customers.
The company has plans to expand into other areas in UK by acquisition of small exciting taxi or Minibus hire companies, increasing business performance by improving servicing processes are a rapidly growing area of interest and one which typically generates very substantial business benefits. The company has simple booking system and it senior management realised to improve the business activities. The company’s operation manager wants to new IT system to introduce best practices into the organisation. UGO taxi for which I have created the IDEF model is a medium sized taxi and bus company. It involved in a business that provides quality transport service for pre booked journey for individuals and groups. The company business is growing that made company to face difficulty to maximise the efficiency and quality of service, the company while maintaining and the flexibility and responsiveness to the demand generator.
Low resource utilisation which means the vehicle is idle and capital is tied up needlessly.
High unplanned overtime levels which are forced by the need to get late running orders delivered.
Too much stock which leads to excess capital tied up, too many vehicles are in hand but not being used effectively.
A high level of late service deliveries which gives many problems, including inability to retain customers and more expensive service costs.
Inability to identify which impact of changes to the service plan such as additional, high priority orders and mechanical failure.
High cost of labour with many periods when labour is idle.
Description of model:
At the centre of the business is the newly designed computer based ERP system which is an integrated system. IDEF model is the approach towards the implementation to restructure the company to produce and efficient and effective operation cycle- input, control, resource and output carries the real function which will determine the validity of the transformation in the company. It collects data from different functional areas of company such as:


 The inputs data are:
The inputs data are:Regular customers, Ordinary customers
Sales revenue,
Market & service feedback,
Fare,
Fuel, Spare parts etc.
The Control Inputs are:
Vehicle availability,
Service response time,
Business objective & strategy,
ISO 9000
The Resource inputs are:
Computer hardware & software,
Sub company acquisition,
Market research,
New vehicles,
Consumable goods and parts,
Staff & drivers,
Information technology & wireless.
The outputs are:
GPS, www, wireless, free phone,
Customers pick up service,
Publicity and advertising,
Quality service, health & Safety,
Billing and Invoices,
Wastage and scrape,
Wages, salaries & other expanses,
Job creation,
Tax, NI, Vehicle Insurance, MOT,
Service Vehicle.
The raw data of inputs, control inputs and resource inputs to the business that produce output which has shown in IDEF0 model. The company is driven by demand, which may include customers order or sales order forecast. The overall situation can be shown in the attached IDEF model diagram. UGO taxi’s daily basis operation process, the company has launched its new IT based server to make work more effective and reliable.
Business objective and strategy: The ideal is for UGO Company to formulate specific objectives and develop policies, within the frame of general objectives, which together result in co-ordinated and controlled, decision making. To be able to survive, UGO must earn sufficient profits to sell services, of certain quality, at competitive price. A newer approach to consideration of objectives is the ‘stakeholder’ theory which suggests that UGO has responsibility to maintain an equitable and working balance among the claims of the interested groups, i.e. stockholders, employees, customers, suppliers, vendors and the public.
Booking system: UGO has provided various communication services to the customer for booking services. Customer can book their taxi, minibus, wedding limousine car tour and so on through the internet, direct communication with driver, free phone and so on. Customer can access internet and get more and more information which can help them to get information about the company policy and services. They can book through internet which would be cheaper and efficient for customer and the company. It can help the company to maintained the data about the customer i.e. customer status (medium class or rich class, quality oriented or general customer, area and location etc) that can help to company to make future planning and strategy.
Feedback: Feedback involves passing information from one point in a system back to an earlier point with a view to modifying behaviour. Feedback is connected with planning, with its determination of instructions to be used as directives for activities, and the standards for comparison. Control comes from comparison with standards showing the need for corrective action, and analysis of deviation so future plan can be readjusted. The UGO can collect the customer feedback through different source i.e. internet user customer, regular customer, drivers and market survey which will help it for future business planning and service.
Fare: Fare is the main resource for UGO business success. It would depend on the company policy that which type of customer that company has targeted in the market. There would be variety of customer and each customer has different sort of demand, in this case fare would play very vital role. Customer can get information about the fare while they are booking the taxi or minibus through call centre, company’s web site. That will help them to fast and quick information to decide their needs.
Fuels and spares parts: The taxi company always need fuel and the spare parts for driving, maintenance and vehicle servicing. Company can keep data and save millions of pound through this department by keeping the data about the Fuels consumed, Spare parts and the vehicle servicing.
Control and call centre: Control is the back bone of this company in which most of the process is done in this department. Most of the information would be held in this department to give the quality and reliable service to the customer. This department will deal with customer, drivers as well as company’s other department to make the service reliable and convey correct data at correct time by using different IT system e.g. GPS which will help to give the data about the driver’s current position and mileage they travelled, company’s website will help to take customer’s order and feedback which will very important to marketing department. The controller mobilise the driver and try to give good service as customer required.
Allocate work: It deals with the long term request as well as immediate booking. The control IT department can relay that information within a twinkle of an eye by sophisticated computerised system and provide service in the right time with quality service. The company’s IT department can allocate the job to driver by using the software which can help to allocate fast and correct at the right time.
Schedule work:In this process, the company use to allocate the duty and the rota for the driver to give the service. It is basically deal with fleets, company fleet schedule for servicing or repairs more especially due date or period. It handles long term customer request. The company can keep all the data in computer that could help in the future purpose.
Finance department: Finance department generally involve in different operation process i.e. tariff (Fares), buy fuel & spare parts, prepare budget for the taxi company and so on. This department can keep all this information and provide the different information with database to all interested parties. The company’s financial department will keep the employees database and their salaries, vehicle’s database and its associated things which will help to give information to other department in the right time with correct information.
Marketing department: The marketing department generally involved in promotion and advertising. The different associated data and information from different will help the marketing department to do promotion and advertising. Company can target different customer by promoting company’s policy and service. The marketing department associated with job advertising which will help the current market’s for job. The current IT service will help to create job and it will make interested and make the goodwill of company.
ISO 9000: The Company has decided to implement ISO 9000 which will help all the department, staffs and customer to provide correct information and the work in balance and filed. The company will take health, safety and the environment (HSE) issues extremely seriously at the highest level. Safety is always the first item on any work. The company has also going to implement policy which is based on following principle:
*Risk reduction is everyone’s responsible,
*Awareness, involvement and support of all staffs, drivers and customers is essential when identifying hazards and assessing and controlling risks,
*Continuous improvement must be the way of life, with business setting goals and measurements to drive progress.
*To reduce risk and road accident, company will issue driver’s hours and techno graphs.
The business process of UGO can be affected by different factors which have mentioned earlier as well. The business problems listed earlier obviously have successful scheduling system which is essential to develop a detailed, agreed definition of the business problem and enhance of the business process and its associated issues. In addition to consider the physical operations of scheduling within the company and the various business issues included information system. There are two types of information required which may be supplied by other systems, or in some case directly entered into the scheduling system itself. The two types of scheduling system are:
Static data
Number of vehicles,
Number of drivers,
Routes.
Dynamic data
Traffic congestions,
Available vehicles,
Available drivers.
Benefits:
The typical benefits of IDEF model based on demand forecasting of UGO taxi are list below:
Fuel efficiency,
Reduced idle time,
On time pick up and drop,
Efficient allocation of job,
Job creation in the market (Professional)
There are also large numbers of less quantifiable benefits, such as;
Increased quality of service
Reduce response time to customer
Ability to promise pick up
Capacity analysis, e.g. Ability to identify bottlenecks in the systems expansion,
Reaction to problems, e.g. identification of impact of breakdown of vehicles,
Prediction of problems, e.g. where on line booking is linked to a booking control system and can continually re schedule to identify predicted changes in service response as conditions on the any mishap.
The need for IT systems:
The need to improve competitive position is driven by various factors. Some of the most prominent of these are:
National competition: Many taxi companies are finding that they must improve efficiency and service considerably in order to compete with emerging service providers in their marketplace.
Ready to use vehicle: Timeless availably of well maintained and serviced vehicles to provide service is now insisted upon far more than new in many modern companies where quality of service has become the norm.
Increasing service range: market forces are leading to rapid increase in the number of new services which a business must provide.
Based on the keys factors of demand forecasting and IDEF model, we can develop the important technical features and properties from which we can realise the full potential and value of demand.
Conclusion:
The computer based scheduling and demand forecasting system has come of age for almost survive providing sector. Those companies which adopt it can improve their business performance in many areas. Together, these usually provide substantial commercial company is using an on line booking system as well as customer call centre. All the booking information goes into the booking system and then into the central database from where all the data is used by different functional areas. Scheduling system is a system that receives booking information and then plans the work accordingly and gives on-screen schedules to the operations people, so that they can allocate work to the drivers. All the details pertaining to the best shortest routines to the destinations, traffic congestions, mileage, number of vehicles available, number of drivers available, status of vehicles in the maintenance department for serving all that information is available to them by scheduling system.
Conversely, any company which does not optimise its decision support in this area is at immediate disadvantage. The gap between users and non users can only increase as service demands increase, leading to poorer performance and eventually collapse.
Refrences:
Appleby, Robert C, 1991, Modern Business Administration, Pitman Publishing, London WC2E 9AN
International Journal of Project management Vol.20, No.3 April 2002, page 194
International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Vol. 7, No.2, March-April, 1994, page 101
International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Vol.14, No.5, sept-Oct 2000, page 473
International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, vol. 11, no.5, sept-oct 1998 page.416
International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, vol.6 no.4 july-Augt. 1993, page 252
http://www.boc.com/
http://www.gistworld.com/
